Page 15
FIPS Policy
Definition of CSP Modes of Access
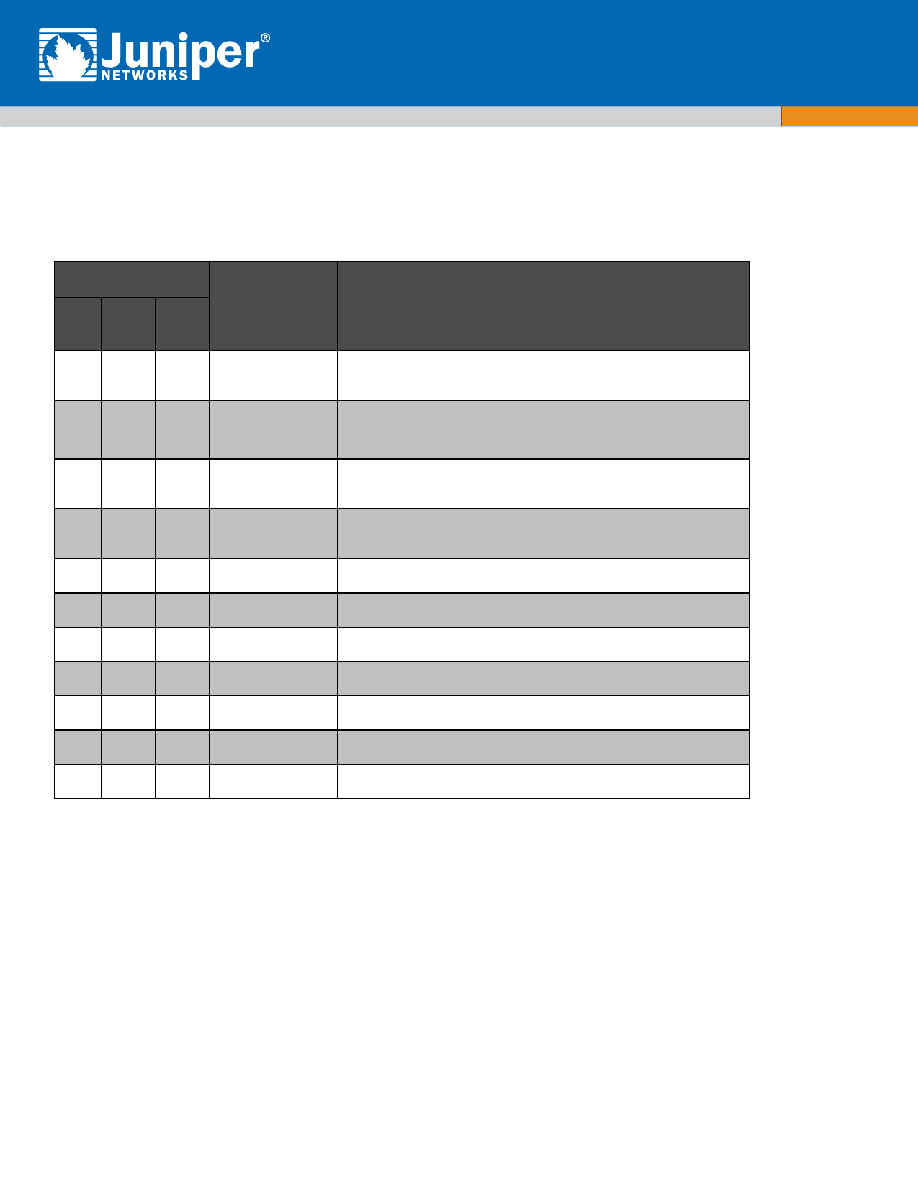
Table 8 defines the relationship between access to CSPs and the different module services. The modes of access shown in the table are
defined as follows:
CSP Access Rights within Roles & Services
Role
Service
Cryptographic Keys and CSP Access Operation
R=Read, W=Write, D=Delete
CO
User
(RO)
User
(RW)
X
Configuration
Mode
All CSPs (R, W, D)
X
Configuration
Mode
Read access to CSPs (R)
X
Configuration
Mode
All CSPs except changing other account passwords (R, W, D)
X
Account
Management
Creates or removes passwords (W, D)
X
X
X
Operational Mode
No access to CSPs
X
X
X
Status Checks
No access to CSPs
X
X
Zeroize
All CSPs (D)
X
X
X
SSH
SSH session key (R)
X
X
X
Console Access
CO Authentication Key, User Authentication Key (R)
X
X
X
Self-tests
No access to CSPs
X
Tamper Seals
No access to CSPs
7. Operational Environment
The FIPS 140-2 Area 6 Operational Environment requirements are not applicable because the cryptographic module has a limited
operational environment.
8. Security Rules
The cryptographic module design corresponds to the cryptographic module security rules. This section documents the security rules
enforced by the cryptographic module to implement the security requirements of a FIPS 140-2 Level 2 module.
The cryptographic module provides three distinct operator roles. These are the User (read-write) role, User (read-only) role and the
Cryptographic Officer role.
The cryptographic module support both role-based and identity-based authentication mechanisms.
Authentication of identity to an authorized role is required for all services that modify, disclose, or substitute CSPs, use Approved
security functions, or otherwise affect the security of the cryptographic modules.
The cryptographic module performs the following tests:
· Power up tests

