Windows Server 2008 R2 BitLockerTM Security Policy
Page 9 of 16
© 2009 Microsoft Corporation
default mode was "require password" if no policy registry key was set. In FIPS mode, the default mode is "no
password" in order to avoid sanity check errors.
If FIPS policy is on (which prevents creation of a recovery password) the error returned by FVEAPI is:
FVE_E_FIPS_PREVENTS_RECOVERY_PASSWORD.
Disallowing both recovery password and recovery key in FIPS mode will allow users to go through the wizard
without a policy error.
To recapitulate:
-
In FIPS mode, no recovery password can be created or consumed. This is because when consuming
a recovery password, BitLocker does not place the volume in RO mode.
-
In FIPS mode, only recovery keys can be used to recover OS volumes (recovery keys or DRAs can be
used for data volumes).
-
In FIPS mode an unlock password (a.k.a. passphrase) can only be created for hybrid volumes (when
the GP for hybrid volumes is turned on). Once such a volume is protected it is RW until it is
unplugged, at which point, if a password is used to unlock it, it will be mounted RO. Hybrid volumes
will always, by design, be unlocked in RO mode on down-level platforms.
-
In FIPS mode, an unlock password (a.k.a. passphrase) can be used to unlock a data volume. If a
password was used to unlock a data volume, the data volume will be unlocked in RO mode.
Once the administrator has configured the policies as described above, and set up BitLockerTM, BitLockerTM
will begin encrypting the operating system volume. Once this conversion process is complete, BitLockerTM will
be operating in FIPS-mode.
Additionally, it is recommended that domain administrators enable the FIPS policy before turning on
BitLockerTM. If FIPS mode is enabled after BitLockerTM was turned on, BitLockerTM must be turned off, and
turned back on in order to remain compliant with the FIPS 140-2 requirements. This is because FIPS requires
that all keys used in FIPS mode should have been created in FIPS mode.
7. Cryptographic Key Management
In order to achieve a higher level of security, without greatly affecting usability, BitLockerTM supports different
types of cryptographic algorithms and encryption layers, including multi-factor authentication. Note that only
a subset of options is available when operating in FIPS mode.
The main goal of BitLockerTM is to protect user data on the Operating System volume of the hard drive. To
achieve this, disk sectors are encrypted with a Full Volume Encryption Key (FVEK), which is always encrypted
with the Volume Master Key (VMK), which, in turn, is bound to the TPM (in TPM scenarios).
The VMK directly protects the FVEK and therefore, protecting the VMK becomes critical. Protecting the disk
through the VMK allows the system to re-key easily when one of the other keys upstream in the chain is lost
or compromised, especially since decrypting and re-encrypting the entire volume is expensive.
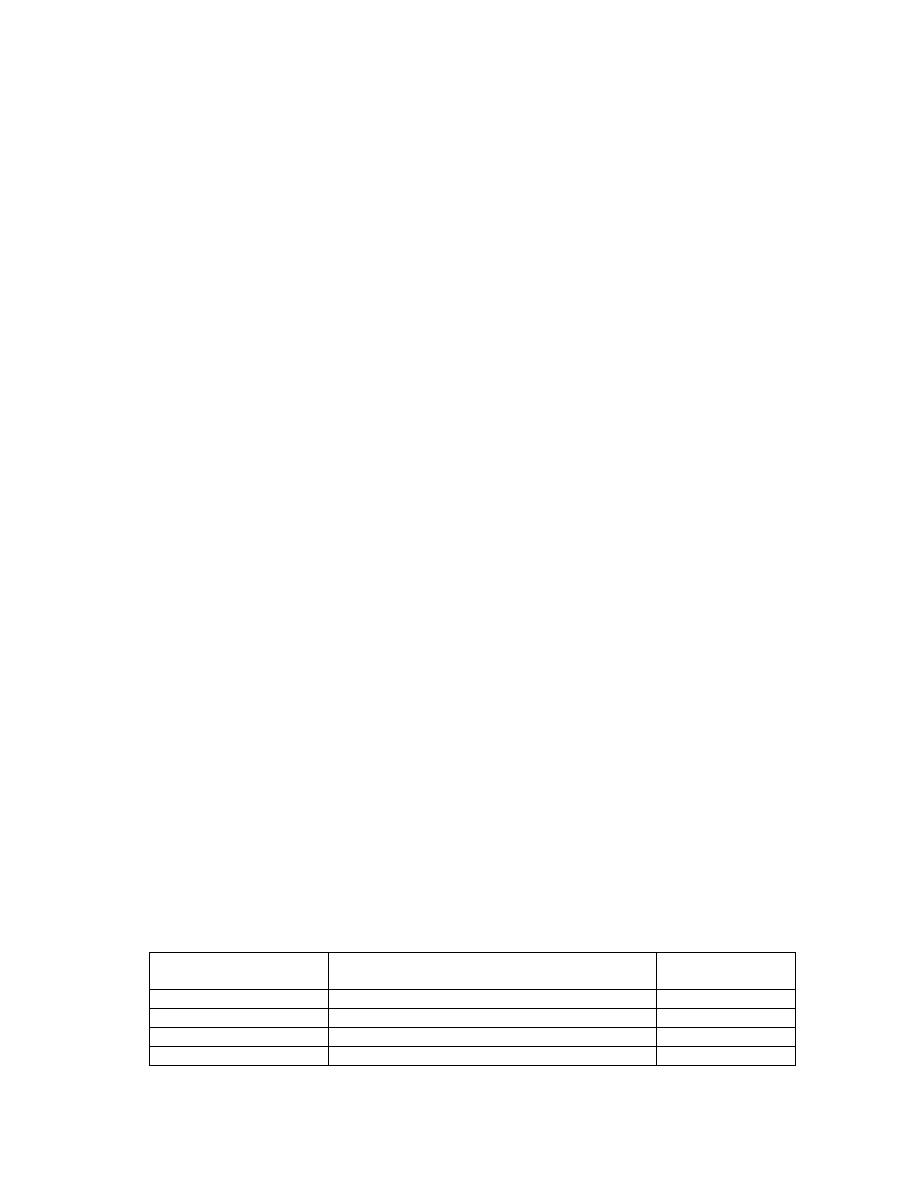
There are several different ways to encrypt the VMK:
Scenario
VMK blob
Algorithm used
to encrypt VMK
Default (TPM-only)
SRK(VMK)
RSA
TPM and PIN
(SRK+SHA256(PIN))(VMK)
RSA
TPM and PIN and USB
XOR((SRK+SHA256(PIN)),SK)(VMK)
AES
TPM and USB (TPM+SK) XOR(SRK(IK),SK)(VMK)
AES

